
Research Paper By Neil Cabral
(Life Coach, UNITED KINGDOM)

Personalities in Coaching
Using personalities as an ecosystem for Coaching
The Role of a Coach
A Coach assists his client in setting goals in line with her values and charting a course to get there. The spotlight is always on the client, with no room for the coach’s preferences, biases or values.
The Coach must be mindful of the following during the coaching journey :
Emotional intelligence is therefore a key strength that every coach must hone. The personality plus model presents a simple and powerful way to understand the client’s motivations and values in the context of her goals. The model also helps the coach understand his own emotional/ personality make up and provides context, especially in areas where judgement may creep in without the coach being aware of it.
The following pages delve into the basics of this model, how it can serve to develop rapport and trust in a coaching relationship. We will also examine how Personality Plus can help with coaching presence, through better self-awareness and a structure to understand and work with emotions.
Does Personality Matter
Why must a Coach consider personalities during the Coaching Journey.
 Florence Littaur, the author of Personality Plus points out that often twins brought up in the exact same environment can have very different temperaments. Children in play-school may exhibit different personalities. Some may be reserved and quiet, afraid to get messy and avoid activities like finger painting in favor of more organized activities like building blocks etc. Some enjoy being the center of attention and like to lead, others prefer to go along and rarely initiate ideas of their own.
Florence Littaur, the author of Personality Plus points out that often twins brought up in the exact same environment can have very different temperaments. Children in play-school may exhibit different personalities. Some may be reserved and quiet, afraid to get messy and avoid activities like finger painting in favor of more organized activities like building blocks etc. Some enjoy being the center of attention and like to lead, others prefer to go along and rarely initiate ideas of their own.
Historical Background
Human interest in personalities goes back to some of the oldest civilizations
Historical background and alternative models
The study of personalities dates back to ancient Greece (around 400 B.C.) Hippocrates was the first to propose that people are different because of differences in their body chemistry. He and other Greek thinkers believed that people could be categorized into four basic groupings and that their differing physical makeup (or “fluids” i.e. black bile, yellow bile, phlegm and blood, in their bodies:) was what caused their personalities to differ. Around A.D. 190, Galen, a Greek physician, build on Hippocrates’s ideas and came up with what he called four temperaments- four personalities or moods that he said were caused by the imbalance between the fluids as proposed by Hippocrates. He called these four temperaments: Sanguine, Choleric, Melancholy and Phlegmatic. The four personality model has served as the basis for various modern offshoots, DISC being one of the better known structures. Other similar models are Merrill-Reid social structure, Larry Crabb, Alessandra & Cathcart, all of while rely on the four personality model, based on Hippocrates’s idea. MBTI is one of the most popular models that classifies personalities into sixteen categories, based on combinations of four traits. MBTI is widely accepted, though it is more complex to understand and apply.
Personality Plus Model
Personality Plus Grouping
Is is possible to divide seven billion humans into four categories. This is not what personality groupings advocate or imply. We are all unique and no two individuals are exactly alike. However, a degree of generalization is evident and helps Coaches understand and appreciate their client’s perspective. This also helps the coach guide the discussion in line with how personalities process information or make decisions. The client will be more amenable to the coach’s assistance if she sees evidence that the coach respects her ‘truths’ or perspective.
The four basic personality types are:
- Popular Sanguine
- Powerful Choleric
- Perfect Melancholy
- Peaceful Phlegmatic
Personality Matrix
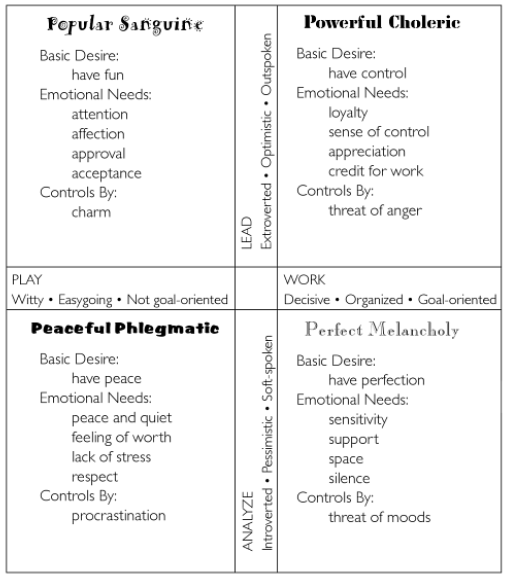 The chart provides an at a glance view of the personalities and their basic characteristics.
The chart provides an at a glance view of the personalities and their basic characteristics.
A brief description of each type is provided in the following pages.
Most individuals display one of these types, which represents their basic personality. And fewer traits from another one of the types. This represents their secondary personality.
You can identify personalities by administering a test.
As you grow more familiar with the system, you could identify personality as you interact with the client.

Popular Sanguine
Using personalities as an ecosystem for Coaching
Traits
These are the fun loving, high energy, out going kind of people.
Desire: to have fun
Key strengths: ability to talk about anything, at anytime, any place, bubbling personality, optimism, sense of humor, storytelling ability
Key weaknesses: disorganized, cant remember details or names, exaggerate, not serious about anything, too gullible and naïve
Emotional needs: Attention, Affection, Approval, Acceptance
Are afraid of: Being unpopular or bored, having to live by the clock, having to keep record of money spent
Like people who: Listen and laugh, praise and approve
Dislike people who: criticize, don’t respond to their humor
Are valuable at work for: their colorful creativity, optimism, light touch, cheering up others, entertaining
Could improve if: they got organized, didn’t talk so much
As leaders: excite, persuade and inspire others; exude charm and entertain; are forgetful on follow through
React to stress by: leaving the scene, creating excuses, blaming others
Recognized by: Their constant talking, loud volume, bright eyes
Living in weakness: Loud, shallow, impulsive, monopolize conversation, undependable, over dramatic, self-centered, superficial, easily distracted
Living in strengths: Energetic, warm, enthusiastic, approachable, inviting, cheerleader
Tips for Coaching
Sample Questions for Goal setting

Powerful Choleric
Using personalities as an ecosystem for Coaching
Traits
These are the ones who like to lead and control
Desire: to have control
Key strengths: ability to take charge of anything instantly and to make quick, correct judgements
Key weaknesses: too bossy, domineering, autocratic, insensitive, impatient, unwilling to delegate or give credit to others
Emotional needs: sense of obedience, appreciation for accomplishments, credit for ability
Are afraid of: losing control of anything
Like people who: are supportive and submissive, see things their way, cooperate quickly, let them take credit
Dislike people who: are lazy and not interested in working constantly, buck their authority, become independent, aren’t loyal
Are valuable at work because: they can accomplish more than anyone else in shorter time, are usually right
Could improve if: They allow others to make decisions, delegate authority, become more patient, didn’t expect everyone to produce as they do
As leaders: they have a natural feel for being in-charge, a quick sense of what will work, a sincere belief in their ability to achieve, a potential to overwhelm less aggressive people
React to stress by: tightening control, working harder, exercising more, getting rid of the offender
Recognized by: their fast moving approach, quick grab for control, self confidence, restless and overpowering attitude
Living in weaknesses: In your face, know it all, angry, bossy, belligerent, argumentative, usurp authority, offensive, controlling, narrow-minded manipulative
Living in strengths: productive, visionary, multitasker, open-minded, leader, organizes people and resources, purposeful/focused, motivates others,constructive
Tips for Coaching
Sample Questions for Goal setting

Perfect Melancholy
Using personalities as an ecosystem for Coaching
Traits
These are the well dressed, organized, meticulous and analytical kind
Key strengths: ability to organize and set long range goals, to set high standards and ideals, and to analyze deeply
Key weaknesses: easily depressed, spends too much time on preparation, is too focused on details, remembers negatives, suspicious of others
Emotional needs: sense of stability, space, silence, sensitivity, support
Are afraid of: no one understands how they really feel, making a mistake, having to compromise standards
Like people who: are serious, intellectual, deep and can carry on a sensible conversation
Dislike people who: are lightweights, forgetful, late, disorganized, superficial, prevaricating and unpredictable
Are valuable at work for: their sense of detail, love of analysis, follow through, high standards of performance, compassion for the hurting
Could improve if: they didn’t take life quite so seriously, didn’t insist that others be perfectionists
As leaders: they organize well, are sensitive to people’s feelings, have deep creativity, want quality performance
React to stress by: withdrawing, getting lost in a book, becoming depressed, giving up, recounting problems
Recognized by: their serious and sensitive nature, well mannered approach, self-deprecating comments, meticulous and well-groomed looks
Living in weaknesses: hesitant, fearful, uptight, fragile, hermit, moody, hypochondriac, emotionally vulnerable, self righteous/aloof, critical, obsessive
Living in strengths: Empathetic, succinct, analytical, organized, compassionate, good listener, reliable, trust-worthy
Tips for Coaching
Sample Questions for Goal setting

Peaceful Phlegmatic
Using personalities as an ecosystem for Coaching
Desire: To avoid conflict, to keep peace
Key strengths: balance, even disposition, dry sense of humor, pleasing personality
Key weaknesses: lack of decisiveness, enthusiasm or energy, a hidden will of iron
Emotional needs: sense of respect, feeling of worth, understanding, emotional support
Are afraid of: having to deal with major personal problems, being left holding the bag, making major changes
Like people who: make decisions for them, recognize their strengths, do not ignore them and give them respect
Dislike people who: are too pushy, too loud, or expect too much of them
Are valuable at work because: they mediate between contentious people and objectively solve problems
Could improve if: they set goals and become self motivated, were willing to do more and move faster than expected, faced their own problems as well as handle those of others
As leaders: they keep calm, cool and collected, don’t make impulsive decisions, are well liked and inoffensive, don’t cause trouble, don’t often come up with brilliant new ideas
React to stress by: hiding from it, watching TV, eating, tuning out life
Recognized by: their calm approach, relaxed posture (sitting or leaning when possible)
Living in weaknesses: Dull, Boring, Indecisive, spineless, lazy, sarcastic, obstinate, passive-aggressive, no initiative
Living in strengths: Loyal, faithful, witty, dependable, steady, consistent, willing, patient, calm
Tips for Coaching

Personalities And Coaching Presence
Creating Awareness
Help build the client’s Emotional Intelligence
A key responsibility of the Coach is to help her client build awareness of her emotions, strengths, weaknesses etc. So that positive behavior is developed and encouraged, and destructive habits and patterns are turned around.
This can begin with helping the client deconstruct her own personality. Why do certain people or patterns upset her, what kind of role does she prefers at work or home. These become clear when the client gets to know her own primary and secondary personality. A basic understanding of other personality types will help her see the motivation and value of those she interacts with and help build emotional intelligence.
Releasing Judgement
The Coach must refrain from judging the client
A fundamental tenet of Coaching at ICF is that the client is creative, resourceful and whole. This means that the Coach has no reason to judge or advise his client. This calls for releasing judgement and pursing a relationship of equals.
Personality Plus can help the Coach get a better perspective to the Coach so that judgement may not cloud his vision. Sometimes we may judge other’s choices or behavior simply because they differ from our own. The personalities help explain the differences in outlook and preferences and this can prove to be the compass that keeps the coaching process free from biases.
Underlying Beliefs
Help the client discover and work through limiting underlying beliefs
All of us form certain underlying beliefs through our unique life experiences. These my sometimes stifle growth if they happen to be limiting or negative.
Underlying beliefs may have a lot to do with how we see the world. This pair of colored glasses becomes apparent through a study of the personalities. The model can be used to make sense of underlying beliefs and help the client come to terms with beliefs that she may have held for long. These can be self-limiting in nature eg. I’m not Athletic or I’m not great with numbers and be a hindrance to growth unless they are recognized and addressed. Personalities can be one of the tools a Coach can use to uncover and address such beliefs.
References
The following books have been referenced
Wired that way : Marita Littauer and Florence Littauer
Personality Plus : Florence Littauer
Personality Plus at work : Florence Littauer and Rose Sweet