A Coaching Power Tool Created by Silky Fischer-Lee
(Executive Coach, SWITZERLAND)
Being Perfect
We often fall into situations in life where we want to be perfect or want to be recognized as perfect with our roles and responsibilities.
Stoeber& Childs (2010, p.577) describe perfectionism as a personality disposition characterized by “striving for flawlessness and setting excessively high standards for performance accompanied by tendencies for overly critical evaluation of one’s behavior”.
Although perfectionism has a negative connotation, it has been perceived as a positive personal trait in many societies. Growing up in a traditional South Korean family, perfectionism had a deep root in my life. Until recently, I thought to strive for perfection in everything I do was a good thing, despite the anxiety I had to deal with.
Not long ago, I had an opportunity to learn more about myself and started to realize the harm that striving for perfection can do to my personal and professional growth.
Perfectionists with self-oriented perfectionism tend to focus on being perfect, motivated by their own needs, and set excessively high standards for themselves. Perfectionists with socially prescribed perfectionism believe that other people have excessively high standards for themselves and fulfilling these standards is a condition to be accepted by others (Stoeber&Chiilds, 2010, p.577). Both self-oriented and socially prescribed perfectionism can lead people to be overly self-critical of their own being. Perfectionism can create anxiety, avoidance, and self-condemnation (GoodTherapy, n.a.). Perfectionists tend to compare themselves to others with unrealistic standards and feel unhappy for others’ success and achievement (GoodTherapy, n.a.). Perfectionism can develop a tendency in people to avoid tasks and situations if they think perfection cannot be achieved. It can also lead people to ignore the important learning process, pushing their focus solely on the result (GoodTherapy, n.a.). Perfectionists develop an aversion toward smart risk-taking.
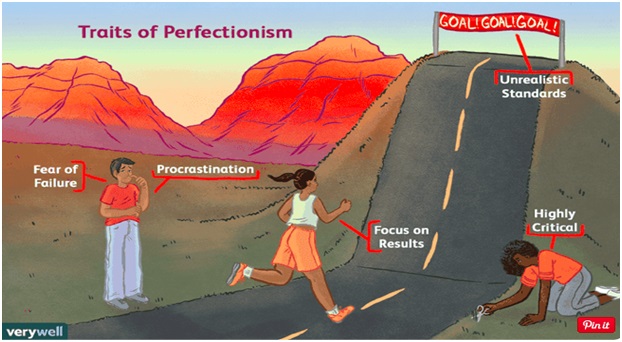 Figure 1. Traits of Perfectionism, Source: Gilmartin B. (n.a.)
Figure 1. Traits of Perfectionism, Source: Gilmartin B. (n.a.)
As Brearley (n.a) points out as below, perfectionism in leadership in the workplace can be counterproductive and can harm the people and the organization’s culture.
Perfectionist leaders can develop narcissistic behaviors described as below (Mayo Clinic, n.a.). These behaviors can appear when they face criticism and can decrease the morale of the team.
Maximizing Your Potential
Focusing on maximizing potential helps people be grateful, joyful, and fruitful for who they are and what they do, despite on-going challenges and issues in life. People who focus on maximizing their potential possess inner peace and strength as a foundation. They have a great awareness of themselves, are not afraid of making mistakes, and are fast to learn from mistakes. They are also comfortable with themselves. Maximizing your potential does not mean neglecting responsibilities in any role they are in. On the contrary, people who strive for maximizing their potential can set goals that are Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Realistic& Timely. This creates actions, which hold themselves accountable for what they want to achieve in their lives. They are also not afraid to take a smart risk.
In today’s highly complex, uncertain, and extremely competitive environment, there is a great demand for leaders who can “build teams, keep people connected and engaged, and drive a culture of innovation, risk tolerance, and continuous improvement” (Abbatiello et al., 2017). These leaders help organizations become living systems. They can “work together, complement each other, and function as a team” (Abbatiello et al., 2017) with a growth mindset. These are leaders who are being at their fullest.
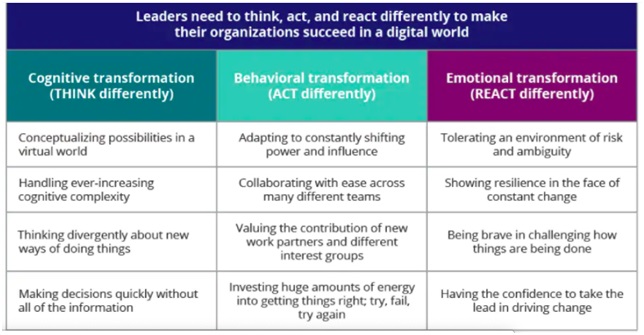 Figure 2. Leadership capabilities needed to succeed in a digital world, Source: Deloitte University Press I dupress.deloitte.com
Figure 2. Leadership capabilities needed to succeed in a digital world, Source: Deloitte University Press I dupress.deloitte.com
The journey to becoming a leader of “being at fullest” involves developing self-awareness and improving self-management skills. Self-awareness and self-management are inseparable and complement each other.
Self-awareness can help you live a more fulfilling and joyful life while being true to yourself. It will enable you to:
Self-management is about “managing your own beliefs, your judgments, your opinions, your reactions” and “knowing how to conduct yourself ”(ICA, 2014). A self-managed person can put her/himself in the driver seat of their own life. With integrity, trust, and honesty they can set SMART goals and adapt to changes in life by proactively initiating actionable plans and holding themselves accountable.
Self Application
There are different ways that you can develop self-awareness and improve self-management skills. Below are some of the examples.
Developing self-awareness (Tjan, 2015; ICA, 2019):
Improving self-management skills (Indeed, n.a.):
Coaching Application
ICF (n.a.) defines coaching as “partnering with clients in a thought-provoking and creative process that inspires them to maximize their personal and professional potential”. A coach supports clients to create self-awareness and improve self-management skills to maximize their potential and growth. Coaching can equip leaders to develop self-awareness and improve their self-management skills. This transforms the organizational culture and enhances employee motivation and engagement.
Building Trust
A coach, a trusted partner, can support the clients to become aware of their thoughts, emotions, and behaviors. As coaches, we believe that people are naturally creative, resourceful, and focus on the whole person (Kimsey-House, et al, 2018).
Active Listening and Powerful Questioning
Powerful questioning can support the clients to create self-awareness and see things from different perspectives (ICA, 2019). It can open up the client’s mind toward other ideas and opportunities. It also supports clients to create their own actions to achieve their goals. Powerful questioning can only happen when a coach is an active listener and fully present, creating a safe space for the client. Coaches must ensure that there are no judgment and assumptions in question.
Effective feedback
Coaches support the clients to develop awareness through effective feedback with no judgment and assumptions involved. Feedback in coaching is simply an observation that a coach has noticed from the conversation with the client (ICA, 2019 a). Effective feedback can help the client get more insight into their thoughts and behaviors.
Self-management
Self-management in coaching requires the responsibility and accountability of both the coach and the client. Both parties are required to be self-managed. While the clients are learning about their own self-management in their role as leaders, by “setting aside personal opinions, pride, defensiveness, needing to look good and being right” and by being fully present for the clients”, the coach can support the client to learn about and improve their own self-management skills (ICA, 2019 b).
StrengthsFinder
StrengthsFinder is an internet-based tool that was developed by Marcus Buckingham and Donald O. Clifton to assess personality from the Positive Psychology perspective. This assessment tool focuses on finding the strengths of the individual and suggests the more suitable development paths based on the strengths. In leadership coaching, StrengthFinder can help managers to (ICA, 2019 c):
Reflection
References
Abbatiello, A., Knight, M., Philpot, S. & Roy, I (2017) Leadership Disrupted: Pushing the boundaries (Online). (Accessed 19 Apr 2020)
Brearley, B. (n.a.) How Being a Perfectionist Leader is Killing Your Leadership (Online) (Accessed 18 Apr 2020)
Gilmartin B. (n.a.) Traits of Perfectionism (Online)(Accessed 19 Apr 2020)
GoodTherapy (n.a.) Perfectionism (Online)(Accessed 18 Apr 2020)
Indeed (2020) Self-Management Skills: Definition and Examples (Online)(Accessed 19 Apr 2020)
International Coach Academy (2014) 10 Rules for Self Management (Online)(Accessed 18 Apr 2020)
International Coach Academy (2019 a) Creating Awareness ( Online)(Accessed 19 Apr 2020)
International Coach Academy (2019 b) Self-Management (Online)(Accessed 19 Apr 2020)
International Coach Academy (2019 c) StrengthFinder (Online)(Accessed: 19 Apr 2020)
International Coach Federation (n.a.) Experiencing coaching (Online)(Accessed: 19 Apr 2020)
Kimsey-House, H., Kimsey-House, K., Sandahl, P. & Whitworth, L. (2018) Co-Active Coaching: Changing Business, Transforming Lives. 4th Ed. Boston. Nicholas Brealey Publishing.
Mayo Clinic (n.a.) Narcissistic Personality Disorder (Online)(Accessed 18 Apr 2020)
Scott, E. (n.a.) Perfectionist Traits: Do These Sound Familiar? (Online)(Accessed 19 Apr 2020)
Stoeber, J. & Childs, J.H. (2010) The assessment of Self-Oriented and Socially Prescribed Perfectionism: Subscales Make a Difference, Journal of Personality Assessment, 92(6), p. 577-585.
Tjan, A.K. (2015) 5 Ways to Become More Self-aware (Online)(Accessed 19 Apr 2020)
