A Coaching Model Created by Sudhir Dhar
(Executive Coach, INDIA)
Why we need a coaching Model:
Coaching models help us to understand the coaching intervention from a systems perspective, and to understand the need for “structure” in the interaction between coach and client. Models help us to develop flexibility as coach practitioners. They offer structure and an outline for both the coaching conversation and the overall coaching journey—whether it is for 20 hours, six months, a year or more. However, although models create a system within which coach and client work, it is imperative that models are not experienced as either prescriptive or rigid.
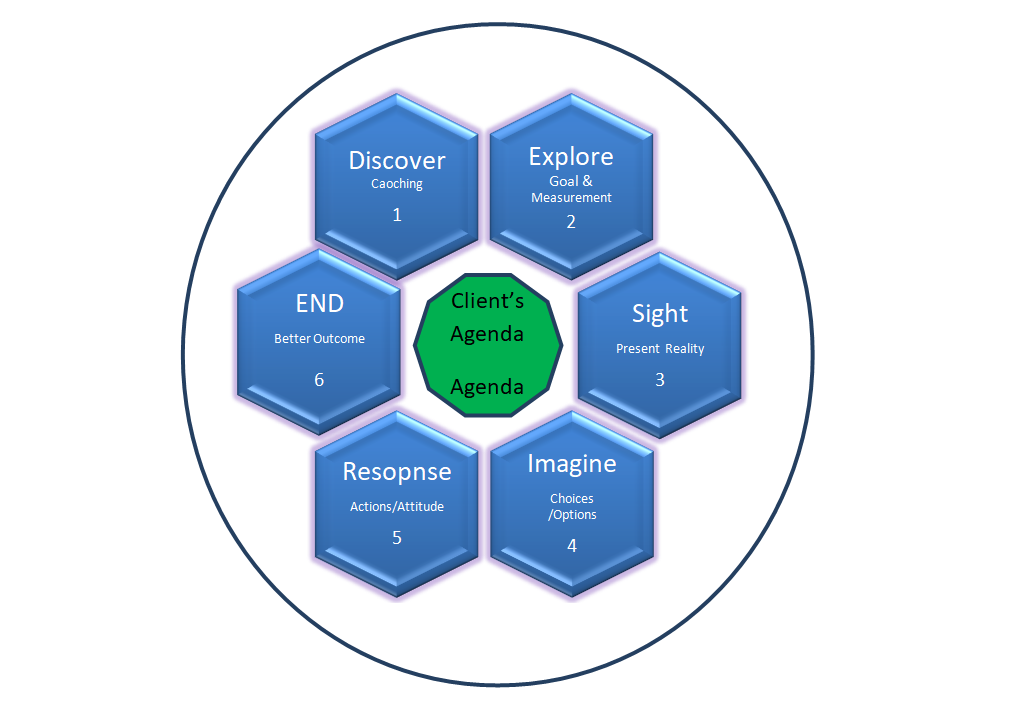
We have been mindful that coaching conversation is about the client, not the coach. If the model is too inflexible, it means the coach has their own agenda to fulfil, rather than attempting to understand the client’s issues.
Discover – Coaching:
Professional coaches provide an ongoing partnership designed to help clients produce fulfilling results in their personal and professional lives. Coaches help people improve their performances and enhance the quality of their lives.” Coaches are trained to listen, to observe and to customize their approach to individual client needs. They seek to elicit solutions and strategies from the client; they believe the client is naturally creative and resourceful. The coach’s job is to provide support to enhance the skills, resources, and creativity that the client already has.”
Explore with discovery session :
Coaching Vs Mentoring Vs consulting Vs Psychotherapy
Coaching for good to great
Coaching agreement for coaching relationship
- Role of coach and client
- What coaching is what coaching is not
- Addressing Ethics and confidentiality
- Client requirement from coaching and his commitment doing so.
Coaching agreement at the beginning of each session
- What to focus on and achieve in a session
- How the client measures success for a session
- Direction is continuing to serve the client.
Explore – Goal &Measurement:
After an initial discussion, establish a realisable goal for the coaching assignment and if required, a target for progress in the session. It is defined as the ability to understand what is required in the specific coaching interaction and to come to an agreement with the prospective or new client about the coaching process and relationship. Often overlooked though is that this competency includes both an initial agreement for the coaching relationship and an agreement at the beginning of each session as to what the client wants to work on, a possible outcome and measure for progress in that time. The initial agreement starts with a conversation on the roles of the coach and the client, what coaching is and what it is not. A written agreement detailing this information as well as addressing ethics and confidentiality is often used and signed by the coach and the client. For a more dynamic written agreement, you could ask your client to add their own paragraph which describes what they want from the coaching and commit to doing.
What is goal for coaching – SMART Goal
Explore motivation of client about Focus /outcome?
Help client to understand their relation to their issue.(Vision , goal , values , strength , beliefs)
How he/she is going to measure progress
What is going to be outcome – “what do you want “
Desired outcome : Subjective or Objective
- Subjective : Plan , Action steps , list of ideas
- Objective : Feeling , stress , more clarity
Sight – Present Reality:
It is important that this session is grounded in reality. The person being coached should be able to assess their present situation, and give concrete examples of their performance to date. Feedback /observation should be shared at this point with proper permission from client. Few sample question Tell me about the current situation? Give me a specific example? What happens/happened when you are there times when it is different? What do you want to change about the way you…?
What is happening
Feeling , emotions , stress
Imagine – Choices /Options :
This stage offers the opportunity for the person being coached to suggest possible courses of action, and together with any that the coach puts forward, these should be evaluated and a choice arrived at. Few sample questions: How could the situation change? How could you improve the situation?
What have you tried so far? What can you learn from others? Can you provide some specific options for action? Are you aware of the possible downsides to those options? Which of these suggested options would you like to try?
What are the options you have to meet your Goal
Response – Actions/Attitude:
The final part of the process involves the person being coached making decisions and having the willpower to commit to them in actions. Future steps to be taken should be confirmed and the coach should agree with the coachee how they will be supported throughout the ongoing development process. Here are some examples of the types of question you could use to conduct the session as productively as possible. How can you put appropriate options into action? Are you aware of any obstacles to these actions? What is the first step? What specifically will you do? What further support do you need? Does your organisation offer support for change? Who do you need to tell/ask? How will we know when you have achieved this? It is important to be aware that at all times in this process the person being coached is being helped to develop their own action plan rather than being directed down a certain route.
Which one options would you like to try first
- If anything were possible, what might you do ?
- What is the structure you will have for you which will keep you on track
- What is the help you would need from other to achieve your goal
- Who all will be ready to help you/guide you during joinery of achieving your Goals?
How will you go about it
- What might get in the way
- How might you overcome that
- What and when is the next Step
End – Better outcome:
Coaching process is a journey, the behaviour which is changed for betterment and huge payoff need to be sustained, hence we need to be mindful of our self-limiting beliefs, values etc. keep structure in place which will client from derailing but same time coach should not become crunches for the client and should be of his own. Below are few benefits client will take over from any coaching intervention.
Considering coaching, here are 12 ways you might benefit:
- Hard results – greater productivity, faster promotions, bigger profits
- Deeper learning’s – about yourself, how you’re perceived, where you can improve
- Faster action – advancing things faster and with greater precision
- Space to hear your own voice – to talk something through and gain perspective
- Awareness of perspectives, beliefs, and attitudes that may be holding you back
- Support and confidence to “lean in” and make bold moves
- Clarity on your values and what you stand for, which leads to greater conviction
- Ideas for ways to improve that you may not see – awareness of blind spots
- Emotional support, empathy, and encouragement – feels less lonely
- The cold truth others won’t tell you
- Third-party moderation for 360-reviews, strategic planning, and conflict resolution
- Support for improving specific skills – communication, delegation, conflict management, team building, persuasion, etc.
In case you are connecting back to client below are the few quick check – in questions :
<<Find out more about how to create your own Coaching model at ICA>>